The name Autophagy is a compound of the Greek terms “auto” which means self, and “phagy” meaning eating, which roughly translates to cells eating their parts (Yun, 2020). This self-cleaning mechanism has thus been proposed as a fundamental activity in cellular homeostasis and disease management. Gradually, it becomes clear that autophagy has a multifaceted impact on the aging process and the development of diseases like cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and cardiovascular diseases, to name but a few (Yun, 2020). More importantly, it has been observed that fasting and dieting induce autophagy, which leads to the renewal of cells, therefore having a positive impact on human health in the long run.
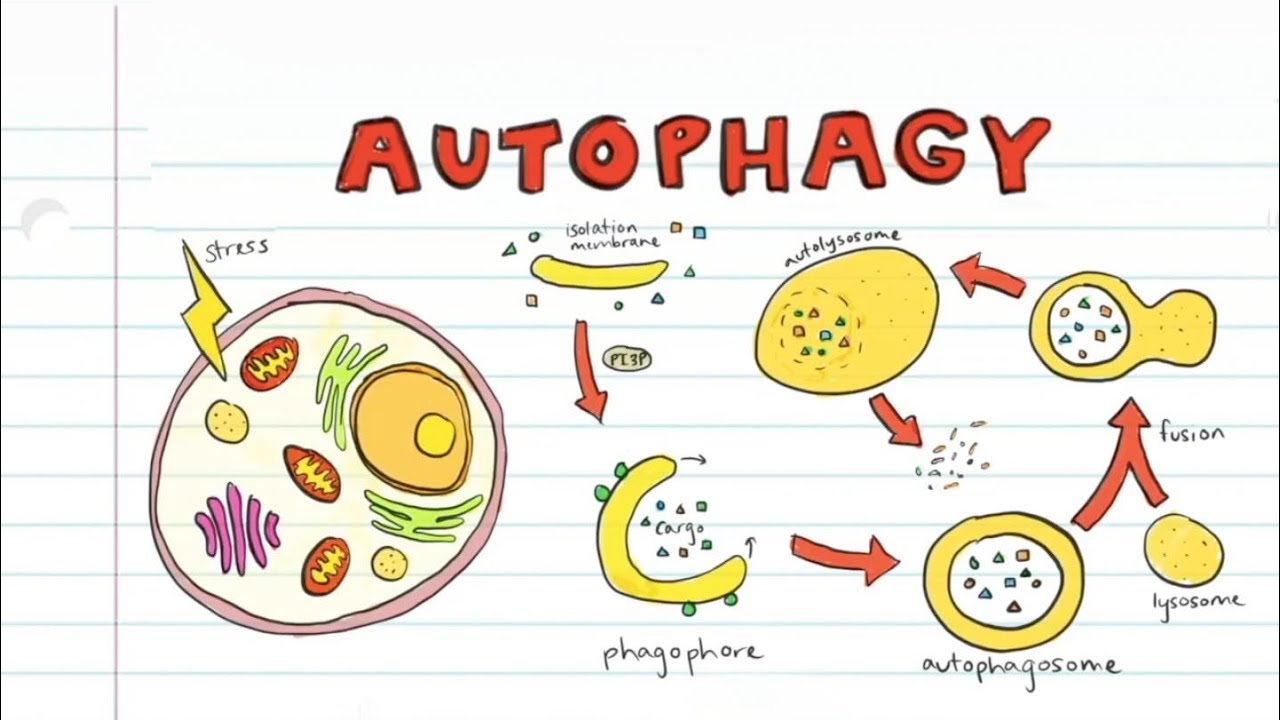
Autophagy in Homeostasis
Autophagy is a physiological state in cells in which cells function optimally by breaking down cellular components that are unnecessary, dysfunctional, or damaged (Ariosa, 2021). In the absence of ample nutrients, cells auto-degrade cytoplasmic structures that are surplus or damaged to synthesize structures for energy or repair work (Ariosa, 2021). This process is important for the removal of dysfunctional proteins, aberrant organelles, as well as invading pathogens. Transportation of cellular structures occurs within the autophagosome, the organelle fuses with the lysosome where the constituents are degraded and recycled (Ichimiya, 2020).
Fasting
Fasting is one of the most effective strategies used in inducing autophagy in the body. Autophagy takes place in the body when food is scarce and the body requires energy to survive; in the process, non-essential or damaged cell components are broken down for energy production (Ichimiya, 2020). This enables the cells to remain functional and alive as far as exterior sources of energy and nourishment are concerned. Various research on human beings has also demonstrated that the process of autophagy is most responsive after 24 to 48 Hours of fasting. Evidence from animal models supports the preventive effects of fasting-induced autophagy on diseases (Nakase, 2020). A cardinal study that was published in the ‘Autophagy’ journal in 2019 concluded that fasting instigated autophagy in mice fabricated upgraded cognitive abilities, memory, and immunizing against neurodegenerative diseases including Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases (Nakase, 2020). There are a few dietary approaches, and one of the most popular in today’s world is intermittent fasting, which is a cycle of feeding and starving.
Autophagy in Disease Prevention
In particular, there has been increasing emphasis on the concept of connecting autophagy to the prevention of illnesses.
Cancer Prevention
Cancer can be described as an unrestricted proliferation of cells, and autophagy has both positive and negative effects on the condition (Debnath, 2023). At the initial steps of cancer, autophagy has the potential to prevent the build-up of abnormal proteins and organelles that give rise to mutations. The meta-analysis conducted by Heland et al in 2018, in nature review cancer evidenced that autophagy inhibits the conditions that cause DNA damage and inflammation that leads to tumorigenesis (Debnath, 2023).
Neurodegenerative Diseases
The major neurodegenerative diseases include Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and Huntington’s diseases, which are characterized by the aggregation of toxic or misfolded proteins in neurons. It is very important in the removal of these proteins and protected neurons. In particular, the results of the research indicate that reduced autophagy contributes to the development of neurodegenerative diseases (Xia, 2021). Most important is the positive regulation of autophagy in the protection of metabolic integrity. A study revealed that learning disability-impaired autophagy can contribute to insulin resistance, the root of type 2 diabetes. A study done on *Cell Metabolism* in 2020 revealed that promoting autophagy in animals reduced insulin resistance and ameliorated obesity-associated diabetes (Xia, 2021).
Cardiovascular Disease
Ischemic heart disease or conditions like atherosclerosis and heart failure are some of the most common both in developed and developing countries diseases that cause death (Yun, 2020). By eliminating damaged mitochondria and other dysfunctional cellular components, autophagy has been found to offer cardiac protection (Yun, 2020). The study conducted in Circulation Research in 2019 noted that autophagy can help attenuate oxidative stress and inflammation in the heart and it is linked with cardiovascular disease.
Diet
It is essential to turn one’s attention to the fact that, apart from fasting, other components in the diet can induce autophagy and make it even healthier (Ariosa, 2021). A pilot study has demonstrated that caloric restriction, a method of reducing daily calorie intake below maintenance level but not starvation, can enhance autophagy and increase lifespan in several animal models. Green tea, turmeric, and blueberries contain polyphenols that have been shown to induce autophagy by enhancing certain signaling paths.
References
Yun, H.R., Jo, Y.H., Kim, J., Shin, Y., Kim, S.S. and Choi, T.G., 2020. Roles of autophagy in oxidative stress. International journal of molecular sciences, 21(9), p.3289.
Ariosa, A.R., Lahiri, V., Lei, Y., Yang, Y., Yin, Z., Zhang, Z. and Klionsky, D.J., 2021. A perspective on the role of autophagy in cancer. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular Basis of Disease, 1867(12), p.166262.
Ichimiya, T., Yamakawa, T., Hirano, T., Yokoyama, Y., Hayashi, Y., Hirayama, D., Wagatsuma, K., Itoi, T. and Nakase, H., 2020. Autophagy and autophagy-related diseases: a review. International journal of molecular sciences, 21(23), p.8974.
Debnath, J., Gammoh, N. and Ryan, K.M., 2023. Autophagy and autophagy-related pathways in cancer. Nature Reviews Molecular cell biology, 24(8), pp.560-575.
Xia, Q., Huang, X., Huang, J., Zheng, Y., March, M.E., Li, J. and Wei, Y., 2021. The role of autophagy in skeletal muscle diseases. Frontiers in physiology, 12, p.638983.


